
-
| 
-
| 
Thylacodes squamigerus (scaled wormsnail) feeds on plankton with
a fishing line of mucus.
|

-
| 
A sabellid polychaete is another suspension feeder, extending its tentacles out of its flexible tube
to catch plankton with a combination of beating cilia and mucus.
,
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
Megathura crenulata (giant keyhole limpet)
|

Melibe leonina (hooded or lion's mane nudibranch)
catches plankton with its expandable oral hood, fringed with sensory tentacles.
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
The gastropod snail, Kelletia kelleti (Kellet's whelk), is an effective scavenger or
predator,here extending its proboscis to feed on a provided fish fillet.
| 
-
|

-
| 
Pleuroncodes planipes (pelagic red crab or tuna crab) is abundant in the ocean
away from the coast, but is not a strong swimmer and can be carried onshore by strong currents, sometimes piled up on beaches.
It is an important food source for tunas and other pelagic fishes.
| 
-
|

The California mantis shrimp (Hemisquilla ensigera)
belongs to a divergent group of crustaceans known as stomatopods, famed for their incredible eyesight and ferocious predatory behavior,
capable of smashing its prey to bits.
| 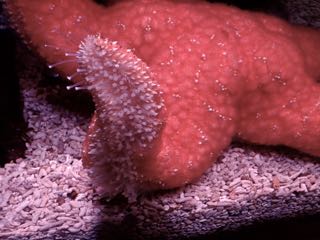
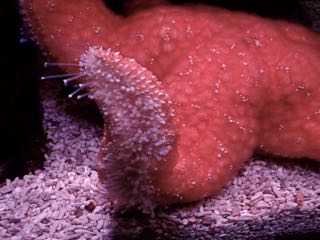
The ochre seastar, Pisaster ochraceus, looks and feels fuzzy underwater because
it extends sack-like skin extensions known as papillae, which help with respiration.
| 
-
|

Parastichopus parvimensis (warty sea
cucumber) feeds like a vacuum cleaner on organic-rich detritus.
| 
The spiny brittle star, Ophiothrix spiculata, occurs in high
densities in some subtidal habitats off California, waving its arms to catch plankton with its tubefeet.
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|
-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|
-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|
-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

The Pacific sand crab, Emerita analoga (Stimpson, 1857), which is widespread on sandy beaches of western North America and
South America, here feeding on plankton with its second pair of antennae.
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|
-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
|
 Under Construction!
Under Construction! Under Construction!
Under Construction!