
We visited the Monterey Bay Aquarium!
| 
-
| 
The MBA provided an informative introduction to the bay and the aquarium.
|

-
| 
We headed right for the otters of course.
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

The kelp forest tank with natural light
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

The sea cucumber, Psolus chitonoides, attaches to a rock like a chiton.
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
Basket star (a highly branched brittle star or ophiuroid) and feather stars (crinoids)
| 
Basket star (Gorgonocephalus eucnemis)
|

Mediaster with crabs
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
Tentative:
| 
Another favorite exhibit 8^)
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

Carnivorous chiton, Placiphorella velata
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

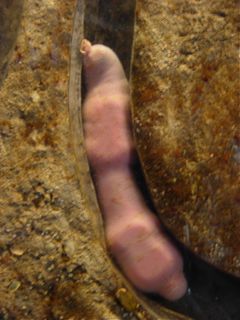
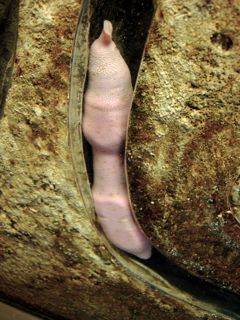
Urechis caupo (fat innkeeper worm, Echiura)
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
Urechis caupo uses a mucus funnel to suspension feed, driving a current through its u-shaped burrow with peristaltic muscle contractions.
| 
It is called a fat innkeeper worm because there are regular commensals, including a scale worm, a clam, and a pea crab. A small fish called a goby is a more occasional visitor. For more details, see here (scroll to near the bottom of this web page). Diarmaid O'Foighil and Dr. Ee have worked on a small clam (Mysella tumida) that also is a commensal but associated with a polychaete's burrow instead (abstract here).
|

This clam might be the commensal clam, Cryptomya sp., well known to take advantage of the "fat innkeeper" and its burrow, actually burrowing just outside the burrow and extending its siphons into the burrow. However, to Dr. Ee, a bivalvaphobic, it looks more like a Kellia sp. (beer bottle clam), which is more of a nestler than a burrower (still under investigation).
| 
Bay ghost shrimp (Neotrypaea californiensis) - see MBA link
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

Female ruddy duck
| 
-
| 
Sand crab, Emerita analaga, is a suspension feeder
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
The sea cave chiton, Cyanoplax caverna, is a small hermaphroditic brooder that is still extremely common in the aquarium splash tank
(see Eernisse, 1988).
| 
-
|

The gumboot chiton, Cryptochiton stelleri
| 
-
| 
Tube anemones (Ceriantharia: Pachycerianthus fimbriatus)
see MBA Link
|

-
| 
-
| 
Moon snail, Polinices lewisii, was seen by Lewis & Clark on their expedition. It is a predator whose drill hole through shells can be recognized even in fossil shells - see here.
|

-
| 
Cobalt blue sponge, otherwise known as Hymenamphiastra cyanocrypta; it gets its color from its bacterial endosymbiont.
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
Wolf eel skull
|

Metridium senile is a suspension feeding anemone.
| 
Fish-eating anemone (Urticina piscivora) - does eat fish but painted greenlings lie in their tentacles, much like clownfish do in tropical anemones.
- MBA Link
| 
-
|

-
| 
Feeding time for the penguins (from S. Africa)
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

Henricia sp. is normally a sponge feeder.
| 
-
| 
-
|
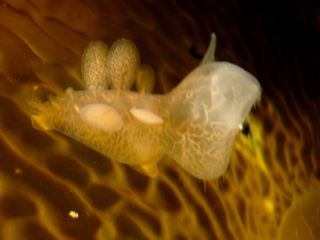
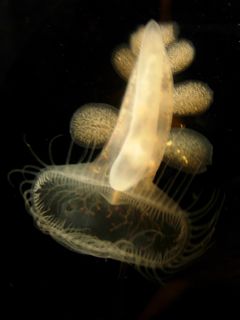
Melibe leonina is a nudibranch gastropod that uses its oral hood to catch plankton. - MBA Link
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

Pacific spiny lumpsucker
(Eumicrotremus orbis)
| 
-
| 
-
|

Ceratostoma foliatum
| 
-
| 
-
|

Cyanoplax dentiens
| 
Lottia limatula (tentative) and Pagurus samuelis
| 
-
|

Black sea nettle (Chrysaora achlyos)
- see MBA Link
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

Calliostoma annulatum, or purple-ringed top snail
| 
-
| 
Tonicella sp. (probably either T. lineata or T. lokii)
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|

-
| 
-
| 
-
|
 Under Construction!
Under Construction! Under Construction!
Under Construction!