 Return to Biology 261 Principles of Zoology Home Page
Return to Biology 261 Principles of Zoology Home Page
Back or  Return to Biology 261 Principles of Zoology Home Page
Return to Biology 261 Principles of Zoology Home Page
Copyright © 2000 D.J. Eernisse. All Rights Reserved.

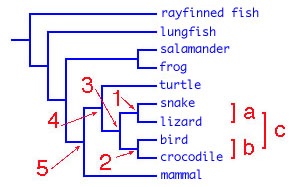
In this example, note that terminal nodes snake and lizard are sister taxa. The branches leading to them meet at node 1
(red arrow) to form clade a (red bracket). Likewise, bird and crocodile are sister taxa. They are members of clade b
who share a common ancestor, node 2, that lived more recently than their last common ancestor shared with clade a, which is at
node 3. According to this cladogram, a bird or crocodile are equally closely related to a lizard (or a snake), because they are related
by way of the common ancestor at node 3. Note also that clade a and clade b are sister taxa. One way to think about this
is to consider the snip rule for dividing clade c into
the daughter lineages derived from the common ancestor at node 3. Imagine traveling up each branch from node 3 only a
short distance before snipping. What falls off are the sister taxa: clade a and clade b.
For practice, can you answer the following questions? What is the sister taxon of the turtle? (*). Which node is the last shared common ancestor of mammal and lizard? (*)
Back or
Return to Biology 261 Principles of Zoology Home Page
 CSU Fullerton, Biological Science
Home Page
CSU Fullerton, Biological Science
Home Page