 Featured
Organisms: Orchids
(Catasetum saccatum shown)
Featured
Organisms: Orchids
(Catasetum saccatum shown)source of image: Darwin's "Various Contrivances…"
Notes for Evolution - The Triumph of an Idea - Chapter 8
Click link to return to Biology
409 Schedule
or back to Chapter 7 or ahead to Chapter
9
General guide on these review questions here
Chapter 8 - Coevolution - Weaving the Web of Life
PBS Website Link: Coevolution
Objectives:
a) Explore different examples of coevolution between different species of organisms
b) Be able to articulate what both coevolutionary partners can gain from a cooperative association
c) Contrast these examples with a coevolutionary "arms race" where one species is exploiting another
d) Relate coevolution to a possible trends in species diversification
e) Draw an analogy between the successful farming by ants and what human farmers attempt to accomplish
f) Characterize a rationale for preserving species that is based on their coevolutionary relationship to other species
Introduction
 Featured
Organisms: Orchids
(Catasetum saccatum shown)
Featured
Organisms: Orchids
(Catasetum saccatum shown)
source
of image: Darwin's "Various Contrivances…"
I. Introduction
RQ Ev-8.1: Contrast the difference with respect to the interests of a flowering plant of producing pollen versus producing nectar. Both can be used as food by visiting insects.
Links on flowering plants and their pollinators: 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7
II. Sexual Go-Betweens
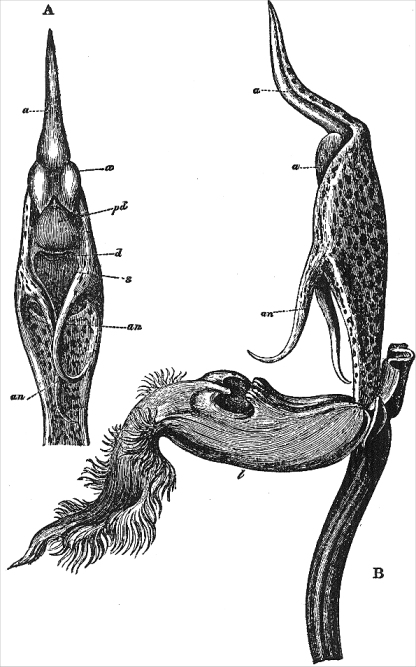
RQ Ev-8.2: What correct prediction did Darwin make in his 1862 book concerning the orchid pollinator that was later named in his honor, Xanthopan morgani praedicta? What was the basis of his prediction?
Links to articles on similar examples here or here
III. The Coevolutionary Matrix
Key Terms: flowering plants (angiosperms)
RQ Ev-8.3: Describe the general pattern of appearance in the fossil record of flowering plants and their primary insect pollinators such as the bees (Hymenoptera), butterflies and moths (Lepidoptera), and flies (Diptera).
Note: Recent surprising evidence, summarized here, suggests that insects had the most dramatic diversification some 100 MY before flowering plants became diverse, and most families of insects did not show appreciable increase in diversity when flowering plants did diversify.
PBS Link to Teaching Guide: Coevolution of Plants and Pollinators
IV. Biochemical Warfare
Link to Edmund ("Butch") Brodie III's Web Site
RQ Ev-8.4: Why does geographic variation in toxin levels support the notion that the coevolutionary interaction between rough-skinned newts and their garter snake predators is like an escalating arms race?
V. Beetles Versus Plants: A 300-Million-Year War
RQ Ev-8.5: Explain Brian Farrell's approach to testing the Ehrlich and Raven hypothesis for a link between coevolution and speciation rate.
VI. Man Versus Bug
PBS Website Link: Antibiotic resistance
RQ Ev-8.6: Why does the EPA expect farmers who are growing genetically engineered Bt-producing crops to plant at least 20 percent of their fields with the same crop species but that are normal, not protected by Bt?
VII. Ants: The First Farmers
PBS Website Link: Ancient Farmers
RQ Ev-8.7: How do leaf-cutter ants manage to utilize up to a fifth of all the leaf biomass in their tropical habitat when they are unable to digest leaves?
VIII. Evolution's Widows
RQ Ev-8.8: How come some fruit-producing plants in Central America, such as Cassia grandis, produce fruits that no animals living with them can successfully swallow to serve as a disperser of the plant's seeds?
Click link to return to Biology
409 Schedule
or back to Chapter 7 or ahead to Chapter
9
This page created 2/3/03 © D.J. Eernisse, Last Modified 4/13/03, Links Last Completely Checked 4/13/03